Posts Tagged Absorption
Eat with your Eyes (and Ears): Acoustic Treatment for Restaurants
Posted by Acoustics First in Absorption, Products, Restaurants on March 21, 2025

When evaluating a restaurant, guests will often look at four factors: food quality, service, price point and atmosphere. The first three are fairly obvious in terms of how they influence the customers satisfaction, but the link between atmosphere and guest satisfaction is a bit murky.
Atmosphere is a sort of “catch-all” term for the various room and design elements that contribute to the overall experience of the patrons. “Atmosphere” is usually associated with visual elements, like lighting, table setting and decorations, but “atmosphere” can literally refer to the air in the room (is the restaurant properly ventilated, are there distracting smells from the kitchen?) or more functional/operating elements like the layout of the tables and, our focus in this article, sound management.
Sound Management – How many times have you been to a busy restaurant that is so loud you can’t hold a conversation with those at your table? It’s difficult to understand speech when background noise and reflections from other sources cover up new information. This causes patrons to elevate their voices to be heard, further exacerbating noise level issues.
Studies show that patrons spend more time and money at restaurants that properly address sound management, ensuring their guest don’t feel overwhelmed at peak hours. Key considerations include:
- Background music: Choose music that complements your restaurant’s concept. Adjust the playlist and volume based on the time of day and desired energy level—soft jazz for a relaxed dinner or upbeat tracks for a lively lunch.
- Comfortable conversation levels: Keep music and ambient noise at a volume that allows guests to speak without straining to hear each other. The right balance creates a welcoming buzz without becoming disruptive.
- Consider layout impacts: Open kitchens, high ceilings, or closely packed tables can amplify noise. Think about incorporating design features like partitions and high booths to help “break up” sound that is traveling from table to table.
- Acoustic design elements: Sound will build up most in spaces that have a lot of hard/reflective surfaces. Use sound-absorbing materials like acoustic panels to reduce reverberation/echoes and create a more intimate atmosphere.
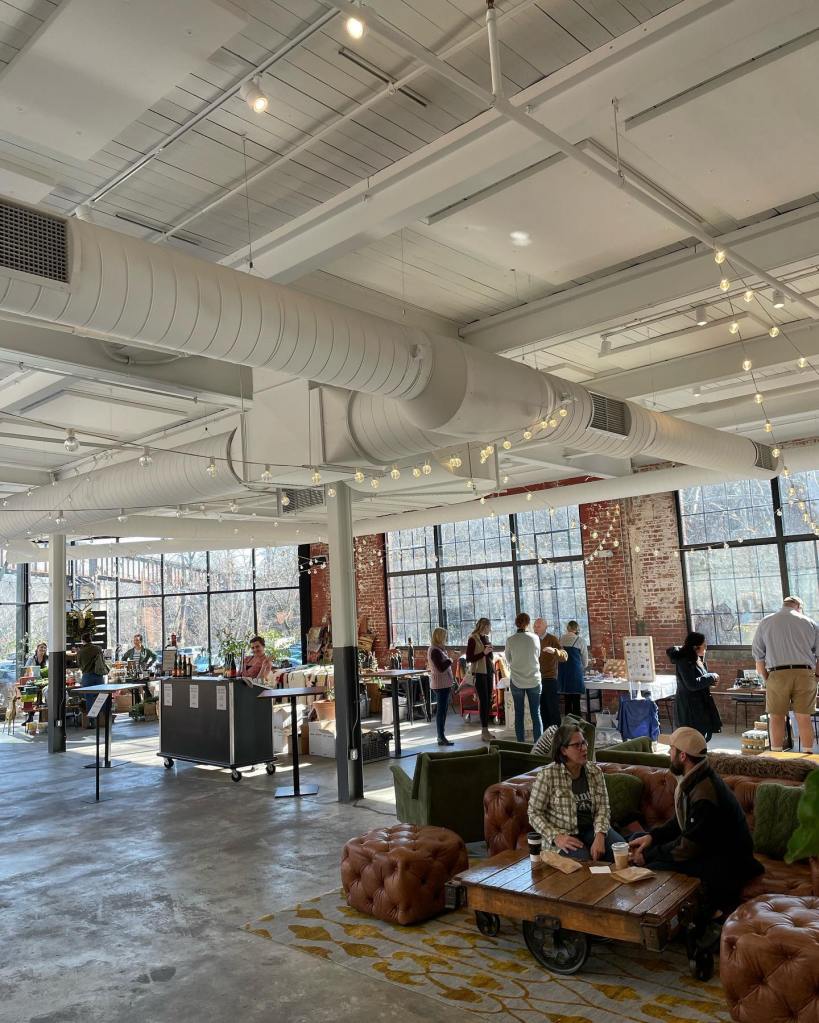

Tone Tile Panels – In restaurants, it’s especially important to minimize visually obtrusive acoustic treatment so it does detract or conflict with the carefully constructed aesthetic of the dining room. Tone Tiles are a perfect solution for restaurants that require “invisible” sound absorption as they can be field or factory painted to match the wall or ceiling color precisely. They also have a white, lightly textured surface that resembles drywall (Tone Tiles can be used as projector screens). Keep in mind, the more you paint an acoustic panel, the less sound reaches the absorptive substrate. We recommend light passes with water based paint to ensure the surface of the panel remains as acoustically “transparent” as possible

Silent Picture Panels – Another popular treatment option is our Silent Picture panels. Silent Picture panels can be wrapped with customer supplied artwork, images or branding. Restaurants love the double utility of full-color images and premium sound absorption.

Can’t I just put foam under the tables? We do not typically recommend acoustic material underneath restaurant tables. Treating the underside of tables will only “take the edge” off overall sound buildup, primarily attenuating sounds produced below the table (shuffling feet, chair slides, etc.). Sound absorptive treatment is much more effective when in the direct “line of sight” of primary sound sources. Also, installing acoustic foam or felt under tables, where it is likely to be picked at or possibly soiled, present durability and sanitary concerns.
We’ve all heard the expression that we “eat with our eyes”; if the meal is not appealing to look at… it is less pleasing to eat. However, we also “eat with our ears”; if the environment is not conducive to comfortable conversation, then the customer will leave with a bad taste in their mouth, even if the food quality and service is exceptional.
Acoustic Treatment in the 1920’s – A look at the Guardian Building
Posted by Acoustics First in Absorption, Offices, Uncategorized on January 14, 2025
The bank wanted the building be a “show-piece” and communicate its principles of “security” and “fidelity” (remember, this was at a time before the FDIC), to impress customers and convince them to store their valuables at their bank. Incredibly, the building was completed in just one year; construction began in 1928 and finished just before the Stock Market Crash of 1929 (so much for fidelity).
Head designer Wirt C. Rowland had far from a subdued vision for the building. Blending Native American, Aztec, and Arts & Crafts designs, Rowland wanted to make an indelible impression on anyone who walked in. He said “We no longer live in a leisurely age…the impression must be immediate, strong and complete. Color has this vital power.”

Colorful, luxury materials grace every surface of this building. Italian Travertine marble was used for steps and wall surfaces, contrasting with deep-red Numidian marble imported from Africa. Brilliantly colored tiles fill the lobby’s vaulted ceiling, and a massive multi-colored mosaic adorns the vestibule wall. Monel metal was used in the large ornamental gate dividing the banking hall and main lobby, supporting a pair of Tiffany & Co. Glass clocks. Even the office corridors and restrooms are lined in a Tavernelle marble from Tennessee.

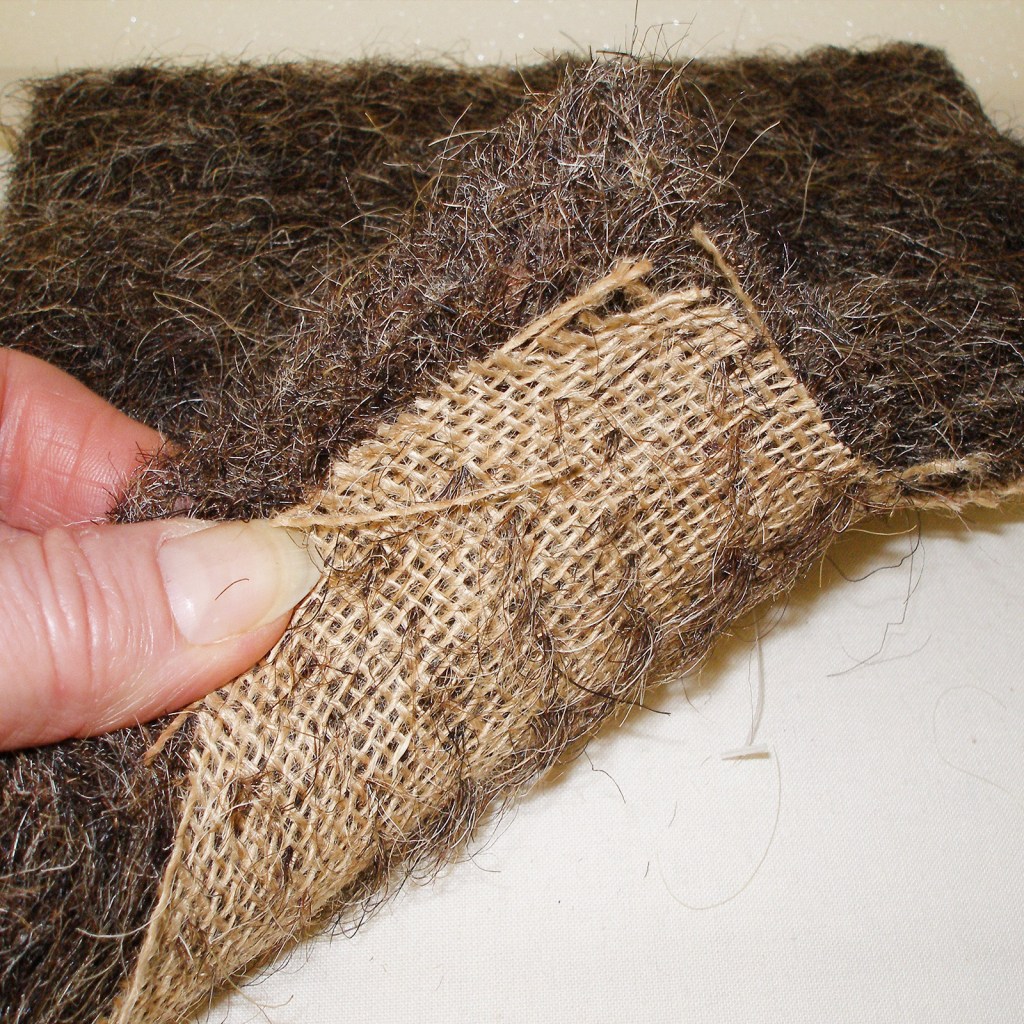
Obviously, these beautiful materials are also extremely sound reflective. Having worked on similar buildings, Rowland understood the need for acoustic treatment in the banking hall as there would be hundreds of customers, tellers and their managers trying to conduct important business in this large, cathedral-like space. If they used the same ceramic tiles they used on the ceiling of the lobby, conversations would be drowned out by a cacophony of typewriters. In lieu of the tiles, the banking hall has an incredibly appointed, intricate system of stretched canvas over wood frames backed with sound-absorbing horse hair. The canvas was hand painted with real gold and silver and requires regular maintenance. In fact, the same Italian family that made the ceiling nearly 100 years ago has been caring for it ever since!

I recently had the pleasure of touring the Guardian building, and walking through the Monel gate from the lobby to the banking hall, you can hear the difference. Though the banking hall is much larger, it feels much more intimate and comfortable, in large part because of the ceiling. Although the horse hair and canvas materials may not meet fire code today, modern stretched-fabric acoustic assemblies owe a lot to this sort of early innovation.

The Guardian Building is a symbol of creativity and achievement. Designed for the future, it is no surprise that Rowland’s masterpiece still dazzles and inspires visitors to this day.
For more information on the Guardian Building’s long history, visit https://www.guardianbuilding.com/history
Similar, yet different: HiPer Panel® vs. HiPer Panel® Impact
Posted by Acoustics First in Absorption, Diffusion, Product Applications, Products on December 11, 2024
While the HiPer Panel® and the HiPer Panel® Impact may appear to be identical on the surface, there are some key differences that may change which one you would use, and why you would use it. They are both layered, flat-panel diffuser products, with perforations, and they are both covered in fabric. However, their construction, below the surface, is drastically different. One is a broadband absorber with a modified frequency response which focuses on reduction of specular energy, and cancellation of noise – where the other is a high frequency diffuser and reflector with a tuned bass absorption which is constructed to maintain acoustic energy in the space.

Construction
The HiPer Panel® was originally designed to optimize the capabilities of a standard broadband absorber. Its internal membrane and perforations create a material that works to modify the range of absorption, and create high frequency diffraction… but that isn’t all. The cavities are backed up to the membrane, which changes the reflection characteristics, where high frequencies can be reflected, and higher energy waves are absorbed more than if it was just fiberglass. This extended range is random, as the perforation density is gaussian in nature, but the membrane is also randomly backed by more cavities.
This design creates 4 different physical conditions that acoustic energy has to contend with… in a gaussian distribution.
- areas of the panel with 2 layers of fiberglass and a membrane in the middle.
- one layer of fiberglass with a rear membrane over a cavity.
- a cavity with a membrane back… sitting on fiberglass.
- a cavity with a membrane back… stretched over another cavity.
The random distribution of multiple acoustic obstacles is what gives this device its unique characteristics. It’s an absorber that changes its performance depending on where sound hits it, and at which frequency. Some frequencies pass into the cavities and reflect off the membrane, while others are dampened by the membrane… while longer wavelengths see the membrane as a stretched diaphragm or limp mass.
The HiPer Panel® Impact has a very different construction and may be used for a very different reason. The HiPer Panel® Impact uses the same pattern of holes, but the holes aren’t cut into an absorber… they are cut out of a reflective face, which is attached to an absober. Unlike the first HiPer Panel®, the “Impact” can be used to maintain more of the energy in the space, break up some of the higher frequencies with that gaussian hole pattern, and be a low frequency bass trap. The design is simple and effective, but is not necessarily used in the same places where you would use the first HiPer Panel®.
Use cases.
The first Hiper Panel® is often used in theaters, and listening spaces where focusing on the source is of primary importance. Its broadband absorption, gentle high frequency diffusion, and smooth mid frequency control are ideal for critical listening environments such as mixing rooms, media rooms, theaters, or even voice over spaces. The performance is about removing the acoustic elements that could interfere with the focus on the source speakers.
The HiPer Panel® Impact is often used in performance spaces, where you want to maintain energy, break up high frequency flutter, and remove low bass. The reflective face doesn’t remove as much energy from the space, however it does change the characteristics of the space. This helps break up some frequencies, reduce bass, and keep the energy moving around the room. Music halls, churches, auditoriums, and any space that relies on the room helping to reinforce the sound will benefit from these taking the edge off the highs and dampening the lows – which is how the HiPer Panel® Impact controls the sound… while helping it maintain its “impact.”
In summary, while these two products are in the same family, they have a different core construction, which changes their performance. There are scenarios where you may use them both, however since they address different problems in a space, they are not always interchangeable. Contact Acoustics First® if you have questions about any of our products.
Acoustical Considerations for Classrooms
Posted by Acoustics First in Absorption, Articles, Classrooms, Product Applications, Products, School & Educational Facilities, Teaching Rooms on September 19, 2024
Poor classroom acoustics has long been the invisible problem that has the farthest reaching implications for learning. Excessive noise and reverberation degrade speech intelligibility, resulting in reduced understanding and therefore reduced learning. In many classrooms in the United States, the speech intelligibility rating is 75% or less. That means, in speech intelligibility tests, listeners with normal hearing can only understand 75% of the words read from a list. Imagine reading a textbook with every fourth word missing. Wouldn’t that make comprehension near impossible? Fortunately, poor classroom acoustics can usually be remedied with some basic knowledge and commercially available treatment. But before getting into specific treatment, let’s go over some basic acoustic principles.
Noise
Obviously, it’s difficult to understand what the instructor is saying when there is a lot of naturally occurring noise in the room. A glut of factors can be considered noise sources, including HVAC “rumble”, traffic outside the building and students moving in their chairs. These sources contribute to a “noise floor” that makes understanding speech very difficult. Since there is no one “cure-all” for an excessive noise floor, it is often best to seek the assistance of a professional acoustical consultant to properly diagnose and find a solution to these issues.
Reverberation: Undesirable vs Useful Reflections
When not attributed to a noise issue, the culprit of poor classroom acoustics is often excessive reverberation. In simple terms, reverberation is the sound energy that remains in the listening environment as a result of lingering reflections. As mentioned before, these reflections can easily interfere with speech intelligibility. As you may have experienced at some point, it can be difficult to understand what is being said when reflections from old information cover up what is newly spoken.
The reverberation time (RT or RT60) is used to determine how quickly sound decays. The RT is dependent upon the volume and surface materials of a given room. Large spaces with hard materials (tile, drywall, etc.) have longer reverberation times, while small rooms built with “softer” materials sound more “dead”. Ideally, classrooms should have relatively short RT’s, somewhere in the .6-.8 second range.
A long reverberation time is not the only factor that should be considered when treating a classroom with poor acoustics. Flutter echo is a particularly significant problem when it occurs between the side walls at the front of the classroom where the teacher is speaking. This condition can be heard as a “ringing” sound (when one claps) as the sound rapidly bounces back and forth between two parallel walls. Flutter and other discrete echoes are considered “undesirable reflections” and should be controlled with absorptive or diffusive materials.
Not all reflections are bad though. There are “useful reflections” that reinforce spoken word, rather than cover it up. The teacher’s voice can be propagated throughout the room by shaping a sound reflecting gypsum board ceiling over the front of the room or by making the center of the ceiling a hard, reflecting surface (see figure 1). This will help project the speaker, so they don’t have to strain their voice to be heard over the students.
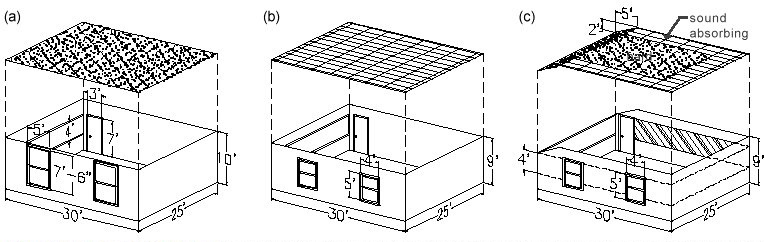
Reducing Reverberation
Often reducing the dimensions of a classroom to attain a more suitable reverberation time is not feasible, but one can improve the acoustics by introducing sound absorptive materials. Typical classrooms usually have a dropped “acoustical” ceiling that has some absorptive qualities. In classrooms that don’t have this ceiling, reverberation can be reduced by installing an acoustical ceiling or a number of fabric faced fiberglass panels, like Sonora® Ceiling Clouds. Likewise, if there isn’t carpeting in the room, you can marginally reduce the reverberation time by installing sound absorptive flooring.
Wall treatment: Acoustic Panels
If the ceiling and floor are at least rudimentarily treated, then hard walls are usually at fault for poor speech intelligibility. Absorptive wall panels, like Acoustics First Sonora® panels, are a common treatment to control lateral reflections and reverberation.
These panels are popular because they can be customized with a variety of colors, edge designs and fabric facings. They also can come with a high-density fiberglass adder that improves durability. In classrooms, these “Hi-impact” panels are particularly useful because the adder allows for the panels to be used as tack boards. This brings an extra level of functionality to the panels outside of their absorptive properties.
Though wall panels are a perfectly suitable treatment, uncovered areas between the panels can sometimes allow a few hard reflections and/or flutter echo to still occur (although full treatment of the walls would likely result in a room sounding too “dead”). For these situations, Acoustics First often recommends Sound Channels® acoustic wall fabric.

Acoustical Wall Fabric
In many instances, acoustic wall fabric is actually a viable alternative to traditional wall panels. Unlike a typical “wall carpet”, Sound Channels® is made of 100% recycled content and has ridges to increase surface area and absorption. Perhaps most importantly, the uniform coverage you get by treating the walls with acoustic wall fabric eliminates the flutter/slap from reflective parallel walls (without making the space too “dead”). Acoustic wall fabrics are generally light weight and most can be put up just like any other wallcovering.

Also of note are the additional benefits when using Sound Channels® in early education classrooms. The effective range that this wall fabric controls is the higher speech frequencies, which is the ideal range for classrooms with younger children (there are not many bass/baritone kindergarteners). Another advantage is in keeping the treatment clean. Wall panels may suck up sound, but they can also absorb fluids (like the occasional juice box). Sound Channels®, on the other hand, is resistant to moisture, mildew and rot. It is also is non-allergenic, easy to clean, and is highly resilient to common wear.
Acoustical Considerations for Classrooms
Although this knowledge has been around for decades, classrooms across the country continue to be plagued by a lack of acoustical forethought. Perhaps as this information becomes more readily available to architects, contractors, administrators and teachers we will begin to see (and hear) better sounding classrooms. School is challenging enough on students and teachers as it is, let’s not compound their daily obstacles by continuing to overlook classroom acoustics.
(Originally published in Christian School Products Magazine – November, 2015)
St. Mary Magdalen Worship Center – Kerfed panels to fit curved walls!
Posted by Acoustics First in Absorption, Product Applications, Products, Worship Facilities on June 28, 2024
The Mary Magdalen Mission Center has an oval-shaped sanctuary that was experiencing extremely poor speech and music clarity. Their Worship services are traditional leaning (spoken word, piano and congregational singing) with the occasional contemporary music service.

Parabolic Focusing – A primary feature of the sanctuary are 4 large curved walls (two at the front and two at the rear). Concave, uniform, curved surfaces are very problematic in room acoustics. Curved surfaces “focus” sound reflections to a point, akin to a magnifying glass focusing light passing through the curved lens.
If you’ve ever stood in the center of dome, you’ve probably experienced a few interesting acoustic anomalies. First is the “whisper” effect, where sound produced near the foci of the dome/curve, is amplified, allowing a faint whisper to be heard throughout the room (and conversely, all the sound produced in the room focused to this point, causing a cacophony of reflections at the center foci) . Another is the “creep” effect, where sound produced at the edge of arc, travels along the curved surface, losing little energy until it reaches the opposite end of the arc.

Not only do the hard wall and floor surfaces of the Mary Magdalen Mission Center contribute to excessive sound buildup, but the parabolic focusing from the curved wall surfaces caused extreme comb filtering (pockets of destructive and constructive interference as a result of overlapping waves), exacerbating intelligibility issues. These conditions contribute to an acoustically uncomfortable environment in which music is hard to perform and enjoy while speech is also difficult to understand.
To significantly reduce excessive reverberation and destructive reflections, we recommended installing approx. 1200 SQFT of 2” back-scored Hi Impact Sonora Wall Panels across the rear wall surfaces. We specified kerfed/back-scored Hi Impact Sonora Wall Panels that can “bend” to fit curved surfaces and come with a high-density adder that improves acoustic performance and durability. View Sonora Panel information on our website.
https://www.acousticsfirst.com/sonora-wall-panels.htm
Reverb Predictions – Worship spaces of this size with a blend of traditional and contemporary music should have a reverb time below 1.6s. We entered the room’s dimensions and construction materials and made a prediction of reverb times before and after treatment. In addition to controlling distracting echoes and comb filtering, installing approx. 1248 SQFT of 2” Hi Impact Sonora wall panels across the rear wall reduced reverberation by approx. 35%, significantly improving speech intelligibility and music clarity.
You must be logged in to post a comment.