Posts Tagged acoustics first
You say “Diffuser,” I say “Diffusor”
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Q&A, Uncategorized on November 11, 2025
If you’ve spent any time around acoustic treatment—especially sound diffusion—you’ve probably noticed something odd: sometimes the product is called a “diffuser“, and other times it’s a “diffusor“. For newcomers, this can feel like a secret code or a subtle technical distinction – But the truth is much simpler.

Many trace the dual spelling back to Manfred Schroeder, the German physicist who developed the mathematically designed Quadratic Residue Diffusor (QRD).
In German, the word is spelled “Diffusor.” When Schroeder’s work entered the academic world, the spelling likely came with it.
Because his research became foundational in architectural acoustics, the German spelling spread through physics papers, textbooks, and graduate-level acoustics programs. Over time, “diffusor” became a common spelling when discussing mathematical or Schroeder-style diffusors specifically.
As manufacturers began producing these mathematically derived designs—like the ArtDiffusor® line from Acoustics First® (and many other early products)—they retained the “diffusor” spelling as a nod to the academic and scientific origins.
Before long, the industry ended up with two spellings that referred to the same thing:
- Diffuser – the standard English spelling
- Diffusor – the academically inherited, German-influenced spelling tied to Schroeder’s work
Both spellings appear throughout the professional audio world, and both are correct.
Is There Any Practical Difference?
No. None. Zero.
There is no technical difference between a “diffuser” and a “diffusor.” They both refer to devices used to redistribute sound energy and improve the acoustic quality of a space through accelerating the development of sound field diffusion. The spelling variation is purely linguistic.
Think of it like “colour” vs. “color” or “flavour” vs. “flavor.” British English keeps the “u,” American English drops it. (However, if you ask a Brit, they’ll tell you Americans are obviously spelling it wrong.)
The “diffusor/diffuser” split works the same way—just with a German twist.
So Which Should You Use?
Use whichever feels natural or matches the context you’re writing in. Many engineers and academics use “diffusor” when referring to Schroeder-type or other mathematical designs, simply out of tradition. Others stick with the standard English “diffuser.”
Tomato. Tom-ah-to.
Eight very different 2′ x 2′ sound diffusers.
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Product Applications, Products, Recording Facilities on June 30, 2025
Acoustics First® has maximized the idea of adaptable designs. One of the most common modular architectural elements is the 2′ x 2′ ceiling grid. While standard, fiber ceiling tiles have their uses, specialized acoustic environments require higher-performing materials – for both absorption and diffusion. While Acoustics First® excels with its Sonora® and Cloudscape® Ceiling tiles, today we are going to focus on the wide range of 2’x 2′ diffusers that have been developed over the several decades.
Sound diffusers in a 2′ x 2′ format have several advantages, other than just being placed in a ceiling grid to help diffuse the ceiling. They integrate well on walls and in arrays, where they can help break up large flat surfaces and help minimize flutter and standing waves from parallel surfaces. While they provide many different aesthetic options, there are also many different functional types of diffusers available in this form-factor to address different acoustic issues, from flutter, bass issues, targeted frequency absorption, and geometric scattering. Let’s look at some of these devices and their uses.
Geometric Diffusers.
Geometric diffusers have been around a long time. These devices break up large flat surfaces and redirect or “scatter” those reflections in different directions. They work great in environments where you need to redirect acoustic energy in a predictable way, and redistribute a specular reflection over a wider area. In a 2′ x 2′ size, you can also get a fair amount of bass absorption, due to the large cavity behind the geometric shapes creating a space that can be stuffed with absorbent material to tune it.

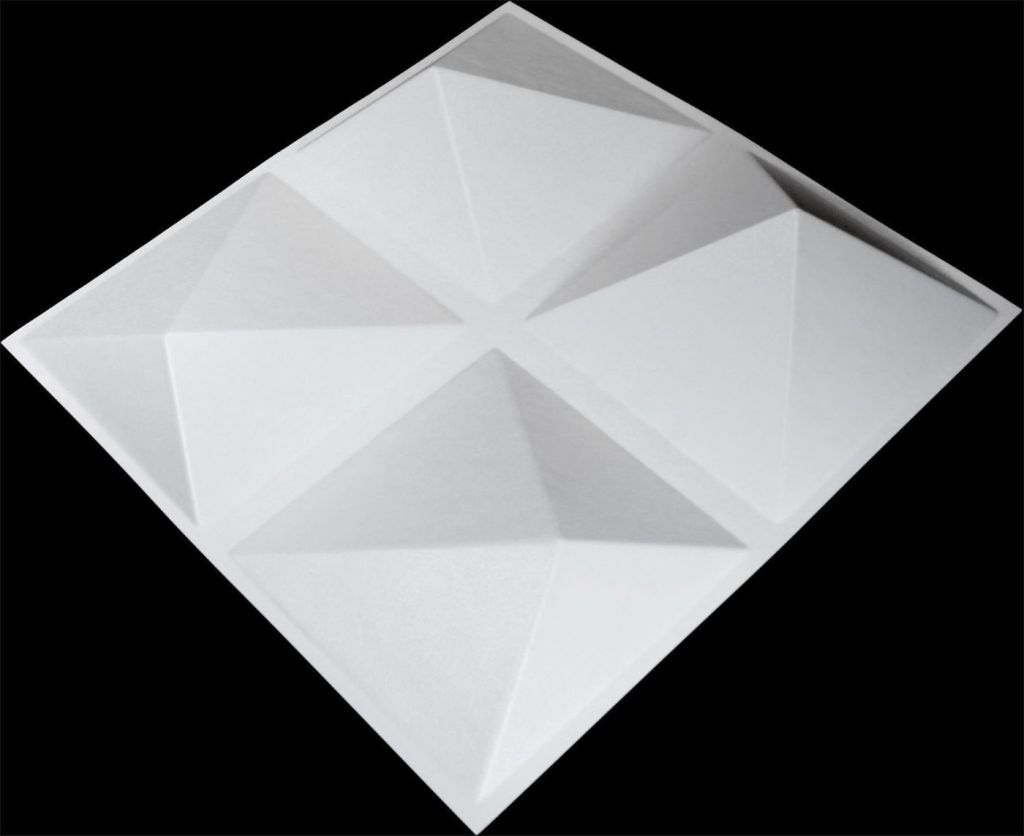
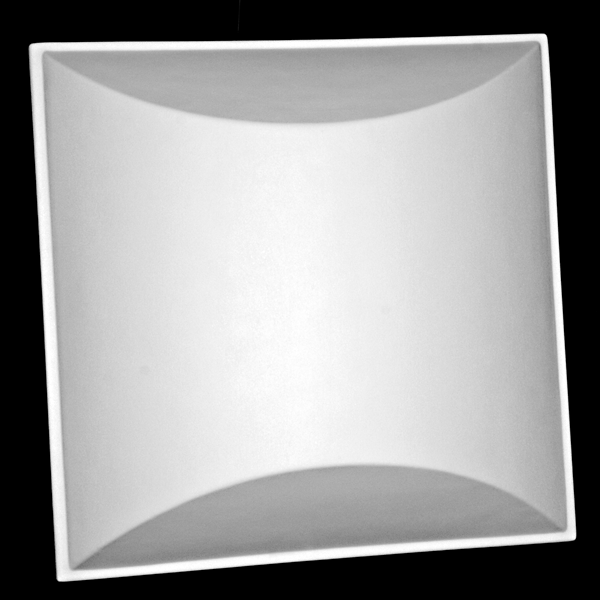
Quadratic/Mathematic Diffusers
Mathematic diffusers are devices that use specific calculations to design their size, shape, and structures to effect their performance. A common type is called the Quadratic Residue Diffuser (sometimes called a Schroeder Diffuser, after its pioneering inventor, Manfred Schroeder). This type uses a Quadratic Residue Sequence that optimizes uniform sound diffusion at specific design frequencies. There are different ways to implement these designs, but two common designations are based on their diffusion patters – 1D or 2D. A 1D Quadratic diffuser mostly spreads energy in one plane, and a 2D provides a hemispheric pattern.



Organic Diffusers.
Organic diffusers are a variation on the classic mathematic diffusers which use different mathematic functions to optimize the diffusion further by creating a smooth transition. Once such method is called Bicubic Interpolation. Instead of having the math restricted to having blocks at certain heights, the interpolation bridges these heights using a function that provides a smooth transition to the next target height. This transition creates unlimited resolution in the frequencies within it’s functional range, providing expanded uniformity throughout its range, and increasing its capabilities. As different frequencies are affected differently depending on their wavelength – the organic diffusers have no hard edges to define their pattern and look differently to different frequencies and energy from varied sources.


These diffusers all have the ability to be used in different types of installations for different reasons. Many of these diffusers are mixed and matched in the same room. You will see these on the walls or ceiling, and placed in different locations. There are rooms with Double-Duty diffusers for low frequency control, Model C for Mids, and Model F for flutter, while other rooms may have Aeolians™ on the rear wall and Model C’s and Model F’s to control the ceiling.

Keep in mind, these aren’t even all the diffusers we have available, these are just the ones specific to the 2′ x 2′ format. The Aeolian™ has a 1′ x 1′ version called the Aeolian™ Mini. There are flat panel diffusers that are hybrid absorbers and diffuser like the HiPer Panel® and the HiPer Panel® Impact. There are even large format versions of the Double Duty™ diffuser, Pyramidal, and even the Quadratic Diffuser.
For more info about these diffusers, read some of our, “Similar, Yet Different Series,” where we go into more detail about our products… and how some of these are similar, yet different!”
If you have any questions as to which products you need to optimize your space, reach out to Acoustics First® and we can help you find which products will be best for your application. Remember that Acoustics First’s® full line of sound diffusers are all made in the USA, with many available in stock for quick shipping.
Absorption & Diffusion – The Construction Specifier
Posted by Acoustics First in Absorption, Art Galleries, Articles, Auditorium, Broadcast Facilities, Diffusion, Home Entertainment, Home Theater, HOW TO, Industrial Facilities, Media Room, Multipurpose Rooms, Music Rehearsal Spaces, Offices, Product Applications, Recording Facilities, Studio Control Room, Teleconferencing, Theater on April 29, 2022
For the May 2022 edition of “The Construction Specifier,” Acoustics First was asked to illustrate the use of absorption and diffusion in creating optimal acoustic spaces. The article is a great reference for understanding the types of acoustic absorbers and diffusers, as well as some use scenarios like offices, critical listening spaces, and larger communal spaces.
Note: This version has been edited and the advertisements are removed. The full published version of the May 2022 digital edition can be found on The Construction Specifier’s website here.
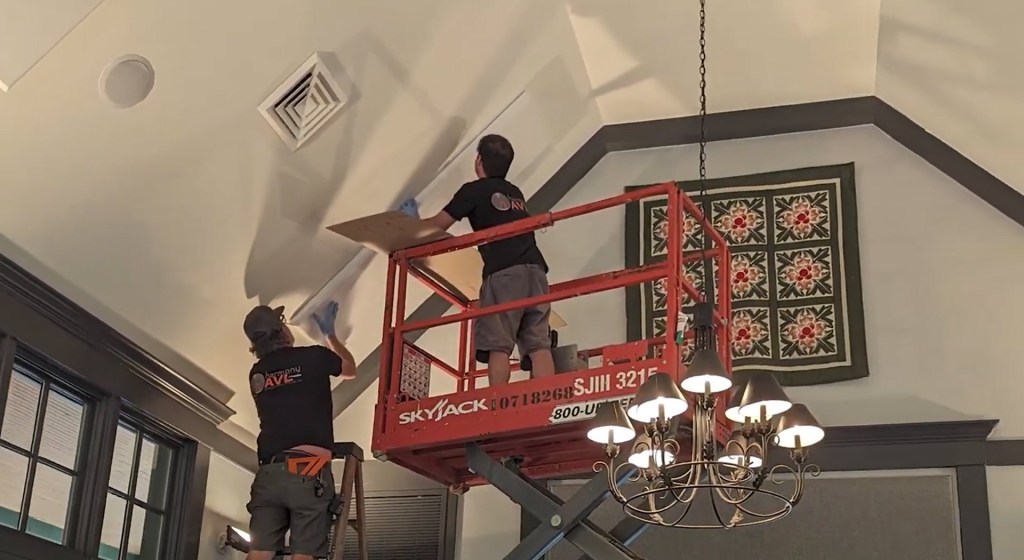
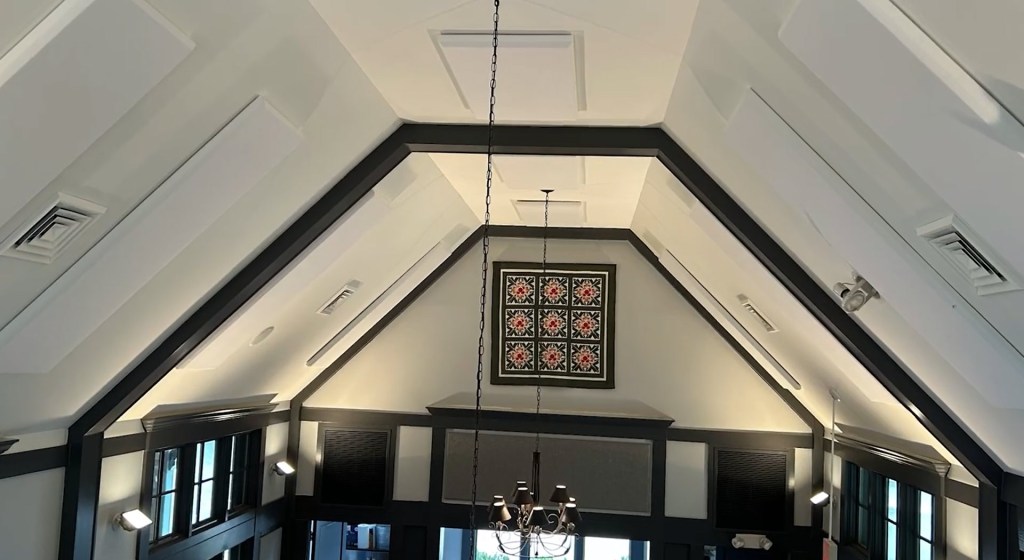
Sonora® Panels help Citizen Heights Church
Posted by Acoustics First in Absorption, Articles, Product Applications, Worship Facilities on July 13, 2021

Citizen Heights Church found a great facility to move into, even during a global pandemic. However, a major obstacle was that the facility had a traditional cathedral ceiling and a nearly 6 second reverb time was not compatible with their high-energy modern services. To address this issue, they included custom Sonora® panels in their overhaul. This decision helped take their 6 second reverb time down to an incredible 1.5 seconds – creating a space that maintains a level of intelligibility which would have been impossible otherwise.
Read the full story here.










You must be logged in to post a comment.