Posts Tagged model c
Eight very different 2′ x 2′ sound diffusers.
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Product Applications, Products, Recording Facilities on June 30, 2025
Acoustics First® has maximized the idea of adaptable designs. One of the most common modular architectural elements is the 2′ x 2′ ceiling grid. While standard, fiber ceiling tiles have their uses, specialized acoustic environments require higher-performing materials – for both absorption and diffusion. While Acoustics First® excels with its Sonora® and Cloudscape® Ceiling tiles, today we are going to focus on the wide range of 2’x 2′ diffusers that have been developed over the several decades.
Sound diffusers in a 2′ x 2′ format have several advantages, other than just being placed in a ceiling grid to help diffuse the ceiling. They integrate well on walls and in arrays, where they can help break up large flat surfaces and help minimize flutter and standing waves from parallel surfaces. While they provide many different aesthetic options, there are also many different functional types of diffusers available in this form-factor to address different acoustic issues, from flutter, bass issues, targeted frequency absorption, and geometric scattering. Let’s look at some of these devices and their uses.
Geometric Diffusers.
Geometric diffusers have been around a long time. These devices break up large flat surfaces and redirect or “scatter” those reflections in different directions. They work great in environments where you need to redirect acoustic energy in a predictable way, and redistribute a specular reflection over a wider area. In a 2′ x 2′ size, you can also get a fair amount of bass absorption, due to the large cavity behind the geometric shapes creating a space that can be stuffed with absorbent material to tune it.

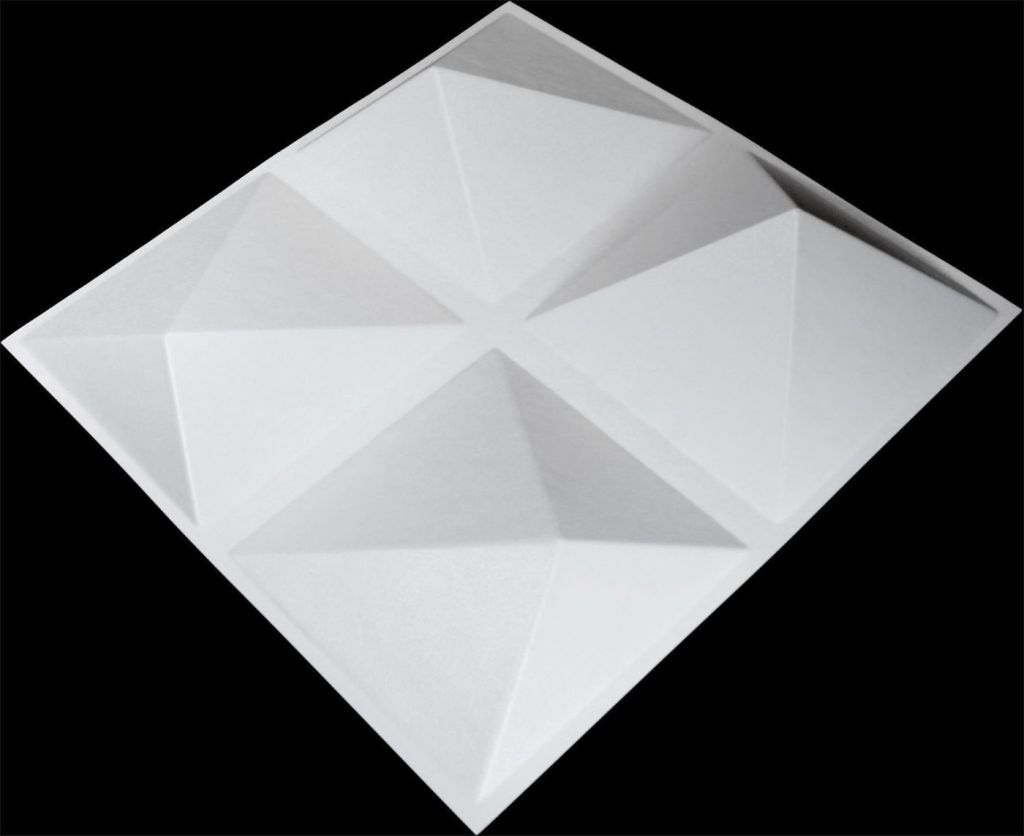
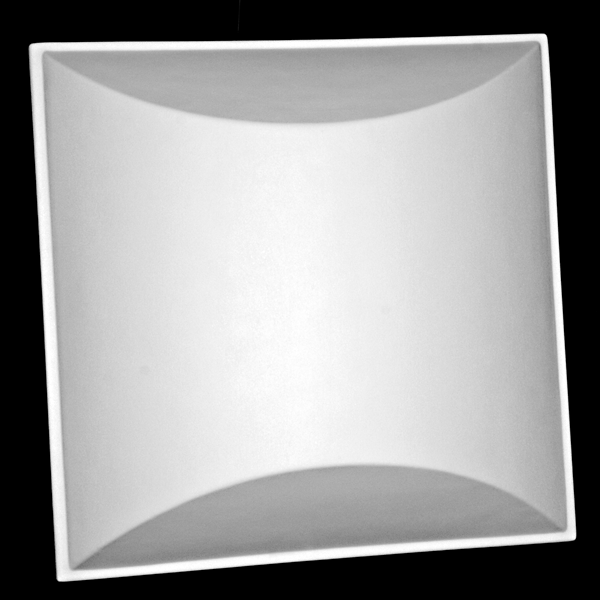
Quadratic/Mathematic Diffusers
Mathematic diffusers are devices that use specific calculations to design their size, shape, and structures to effect their performance. A common type is called the Quadratic Residue Diffuser (sometimes called a Schroeder Diffuser, after its pioneering inventor, Manfred Schroeder). This type uses a Quadratic Residue Sequence that optimizes uniform sound diffusion at specific design frequencies. There are different ways to implement these designs, but two common designations are based on their diffusion patters – 1D or 2D. A 1D Quadratic diffuser mostly spreads energy in one plane, and a 2D provides a hemispheric pattern.



Organic Diffusers.
Organic diffusers are a variation on the classic mathematic diffusers which use different mathematic functions to optimize the diffusion further by creating a smooth transition. Once such method is called Bicubic Interpolation. Instead of having the math restricted to having blocks at certain heights, the interpolation bridges these heights using a function that provides a smooth transition to the next target height. This transition creates unlimited resolution in the frequencies within it’s functional range, providing expanded uniformity throughout its range, and increasing its capabilities. As different frequencies are affected differently depending on their wavelength – the organic diffusers have no hard edges to define their pattern and look differently to different frequencies and energy from varied sources.


These diffusers all have the ability to be used in different types of installations for different reasons. Many of these diffusers are mixed and matched in the same room. You will see these on the walls or ceiling, and placed in different locations. There are rooms with Double-Duty diffusers for low frequency control, Model C for Mids, and Model F for flutter, while other rooms may have Aeolians™ on the rear wall and Model C’s and Model F’s to control the ceiling.

Keep in mind, these aren’t even all the diffusers we have available, these are just the ones specific to the 2′ x 2′ format. The Aeolian™ has a 1′ x 1′ version called the Aeolian™ Mini. There are flat panel diffusers that are hybrid absorbers and diffuser like the HiPer Panel® and the HiPer Panel® Impact. There are even large format versions of the Double Duty™ diffuser, Pyramidal, and even the Quadratic Diffuser.
For more info about these diffusers, read some of our, “Similar, Yet Different Series,” where we go into more detail about our products… and how some of these are similar, yet different!”
If you have any questions as to which products you need to optimize your space, reach out to Acoustics First® and we can help you find which products will be best for your application. Remember that Acoustics First’s® full line of sound diffusers are all made in the USA, with many available in stock for quick shipping.
Similar, Yet Different: Model C vs. Model D!
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Home Entertainment, Home Theater, Media Room, Multipurpose Rooms, Music Rehearsal Spaces, Music Tracking Room, Product Applications, Products, Recording Facilities, Recording Studio, Studio Control Room, Theater on January 5, 2024

In this installment of “Similar, Yet Different,” we take a good look at two very different looking diffusers in the 2’x2′ size… the classic ArtDiffusor® Model C and the organic, rippled ArtDiffusor® Model D – while there are some similarities, there are some key differences in how they look (obviously) and how they perform.
Quick Similarities.
The ArtDiffusor® Model C and Model D are both 2’x2′ diffusers which are made to be either wall mounted or installed in a standard drop-tile ceiling grid. They are both formed from a Class A fire-rated polymer in a single piece. Both are mathematical diffusers, which create their different physical features in a “form follows function” methodology. They also cover roughly the same frequency bands, with some minor variation in how they execute their control.
Difference in Math
The Model C is an interesting configuration. Often you will see quadratic residue diffusers with flat blocks or wells in a relatively standard quadratic cell formula configuration. The Model C runs in a much different alternating binary configuration. The basic idea is that cells are placed in a 45° array with each cell adjacency calculated as an alternating array of higher and lower cells starting in the middle and working in a pattern of alternating low/high cell clusters decreasing toward the edges of the diffuser. These diffusers also do not have flat tops on the blocks – they are angled at 10°. The orientation is then rotated in 90° steps in a pattern that maximizes the spatial redistribution of reflected sound. This was a vast design departure over the original quadratic design, and created a diffusion profile that was distinctly different.

The Model D was an even greater departure. It began with a Maximum Length Sequence (MLS) concept that first changed the varied straight channels into rings of different dimensions. These rings then broke from the MLS mold by getting varied height profiles based on the QRD sequence. As if having different size rings at different heights wasn’t enough… the randomness was further perpetuated through a Boolean process of assigning certain rings a random property that would either add or subtract height from any other ring that they crossed. Finally, the entire surface geometry was smoothed using a bicubic interpolation, creating the organic undulating surface which gracefully spans the entire profile.

What this difference in math does to the acoustic performance.
The Model C has a nice even diffusion profile through it’s primary working range. This is a product of the QRD design and binary distribution. The set size for the blocks guarantees a solid primary frequency range from about 1KHz to over 4Khz. This tunes the Model C squarely in the most sensitive bands of the human hearing range. Below this range the device becomes a bit of an absorber. Above this range and the performance becomes more effective at intervals, which can be seen in the areas of wide diffusion at 6KHz – 18 KHz. These repeating zones are common in “stepped” quadratic designs. Due to the heights of the well being at specific intervals, the intervals repeat at octaves of their effective bands.
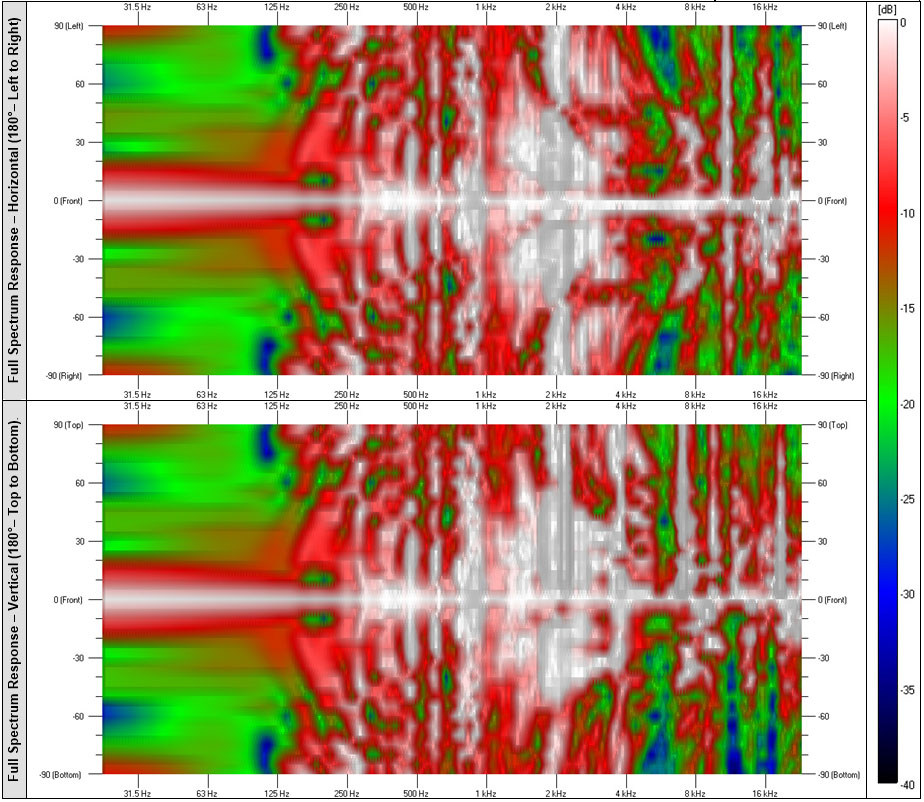
The Model D doesn’t have the same stepping. The spline interpolation and the random Boolean shifts smooth the transition from one quadratic height to the next, and the MLS sequence causes a bit of a high-pass filter pushing the start of the primary range to around 2KHz – which is a little higher than the Model C. The main difference is that once the Model D starts it’s range it diffuses everything up to and over 20KHz without the banding that can happen in other quadratic designs.

Another difference in symmetry.
The ArtDiffusor® Model C is a fairly symmetric design, but it’s 45° angle pushes that symmetry along the diagonal (corner to corner) across the unit. The asymmetry is subtle but allows for enough variation to account for any “lobing” issues that can occur in more simple geometric devices The 10° block faces being at varied orientations is key to increasing the spatial directivity over the older “flat-faced” Quadratics. This was a very novel design when it was first introduced, and those benefits are crucial to the longevity of the Model C’s reign – It just works. It’s predictable and musical… and that’s why it’s here to stay!
The ArtDiffusor® Model D is a completely different animal from the Model C when it comes to symmetry… as a matter of fact… there isn’t really much on it that is symmetric! The Model D was designed as a departure from symmetry. Focusing on the mid to high frequencies, which are very specular, the organic geometry creates an asymmetric reflection pattern. This pattern can be used to steer the sound into a wider field.. and that profile changes with the wavelength of the sound that hits it. This steering ability and the wide frequency range has made the Model D a favorite in mixing and mastering environments, where they can get smooth performance through the entire frequency spectrum.

How these differences benefit everyone.
We have stated before that there isn’t really a one-size-fits-all solution in acoustics. Many environments will use various treatments to achieve their desired goals. You will often have different devices to address different problems, in different frequencies, in different locations, in the same space. Bass traps for controlling the lows. Absorption to reduce gross energy across the board. Large geometric surfaces to break up parallel reflections and steer the projection of sources. Mid range diffusers to create clarity to the sources and reduce artifacts. High frequency diffusers to reduce flutter and add a feeling of envelopment and airiness in the space. These devices all have their place – from the smaller listening rooms, to critical listening environments, and large multifunction spaces and venues.
It is also worth noting that these two devices have a very different aesthetic visually. The classic blocks of the Model C have become a signature look for quality sound environments, and people recognize them as they would classic geometric pyramids and barrels. The Model D aesthetic provides a visual accent that people take advantage of to set their space apart from others. The undulating, asymmetric pattern changes drastically when you rotate the individual units in the array. This allows for not only varied acoustic performance, but also a unique visual possibilities – with numerous variations.

The ArtDiffusor® Model C and Model D are two tools that are used to craft ideal listening environments around the world… and in those roles they are indeed Similar, Yet Different.
ArtDiffusor® Model D vs. Aeolian®: Similar, yet different.
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Product Applications, Products, Uncategorized on November 12, 2020
Today on, “Similar, yet different…” we are going to analyze two more of our acoustic diffusers and compare/contrast their designs and functionality… and this one is a doozy; The Model D vs. The Aeolian®. These two diffusers have some very interesting similarities and some surprising differences – so lets get started!
We have discussed the Aeolian® construction before, so we will start here with a quick recap as a reference point. The Aeolian® started life as a blocky-looking diffuser – just like the Model C, but the implementation is different. While the Model C retains its “blocky” appearance, the Aeolian® has run through a mathematical process called “bicubic interpolation.” This smooths the transition from one block to the next, creating the wavy appearance of the Aeolian® diffuser.
So, keep that in mind: The diffuser was tuned with different height blocks and then the transitions were smoothed.

Look at the smooth curves of the Aeolian®.
The Art Diffusor® Model D has multiple layers of math below its curved surface. While the Aeolian® started life as “Blocks” of different heights… the Model D started life as “Rings” of different sizes and heights. The calculation for the heights is identical to the mathematics used in tuning the Aeolian®, but why different sized rings?
There is an older diffuser design known as a Maximum Length Sequence (MLS) diffuser. These were tuned to different frequencies using a specific depth, and different spacings of “lands and valleys.”
The Model D started with the concept of twisting the MLS spacings into rings, and changing the size of the rings. Then to break the “MLS mold” of having the same depth, this MLS ring structure is raised to different heights using Quadratic Residue calculations… effectively combining the rings of MLS spacings with different QRD heights. While this could have been where this stopped, we wanted to interject more randomness into the equation.
Wherever the rings of different heights intersected, we decided to change the heights by values relative to the difference between the two rings. This height variation is what is responsible for the “random” waviness. This was accomplished with different Boolean Functions, to either add or subtract height where the rings intersected.

You can really see the variation in the geometry of the Model D… look at the ripples in the rings.
This method of using Boolean Functions inserts a known-height randomization into a hybrid MLS/Quadratic system. (That’s a mouthful.) The final step, after refining the ring size, height, position and intersection parameters… was to smooth the whole geometry with “Bicubic Interpolation.” That’s right. This final step smooths all the transitions from the heights, just like the blocks of the Aeolian®.
So onto the Simple Similarities!
Both diffusers use a quadratic residue calculations to get the main heights of the diffusive elements. Both diffusers are finished off with a helping of “Bicubic Interpolation” to smooth it all out. This gives them both a very organic look… The Aeolian® looks a bit like rolling waves, and the Model D resembles droplets of rain in a puddle…
They do perform quite a bit differently though.
The Aeolian® has great lower mid-band performance… while the Model D is a beast in the upper mid-bands starting about 2.5K. The difference is in the severity of the geometry. The Aeolian® is a gently rolling surface which redirects the waveforms uniformly through a wide range of frequencies. The Model D has a very irregular surface. With the different ring sizes, heights, locations and boolean functions… it’s meant to target and shred mid to high frequencies. Both diffusers are asymmetric – and affect different frequencies in different ways.
The Aeolian® is also deeper than the Model D – and this depth is a single resonant cavity… allowing it to be a great bass absorber as well. The Model D is useful in environments where you have bass control in place, but really need to diffuse the upper mid range and bring those frequencies to life… or maybe shred some flutter echos or comb filtering. There are scenarios where both are used in the same environment – but for different reasons.
In Conclusion...
While both the ArtDiffusor® Model D and the Aeolian® both look like liquids frozen in time, they have some other similarities in the math behind them… Yet they are still as different as rolling waves versus droplets of rain in a puddle.
ArtDiffusor® Model C vs. Aeolian®: Similar, yet different.
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Product Applications, Products, Uncategorized on September 24, 2020

For this installment of “Similar, yet different” we look at The ArtDiffuser® Model C and the Aeolian® Sound Diffuser.
While these two diffusers look very different, there are a fair amount of similarities between them. Their physical size and depth allow them both to be great mid-frequency diffusers, but did you know that the Aeolian® started life as a blocky-looking diffuser – just like the Model C? It’s true!

ArtDiffusor® Model C array on a hanging bass trap.
The mathematics behind the two diffusers is similar, but the implementation is different. While the Model C retains its “blocky” appearance, the Aeolian has run through a mathematical process called “bicubic interpolation.” Without turning this into a math-heavy post, if you take a “blocky” design like the Model C and run its geometry through bicubic interpolation, you get a “curvy” surface like the Aeolian® – It “smooths” the transition from one block to the next in a 3 dimensional matrix.
While they did not begin as identical geometries, they were similar in their height ratios – with the Aeolian® starting with fewer blocks in a more random distribution, and a slightly taller maximum height. They both effect similar frequency ranges, with the Aeolian® going slightly lower and higher due to its depth and interpolated surface. The pattern and type of the diffusion is also different because of the different geometries – the Model C has blocks, and the edges of those blocks introduce a great deal of edge “diffraction” – which is what happens when a wave interacts with an edge, or corner, of a surface. It bends and shears around the edge, which helps break up the continuity of the waveform, where the Aeolian® takes the approach of redirecting most of the energy off a randomized and continually-curved surface.

Aeolian® Diffuser array on the back wall of Big3 Studios.
It is important to note that the two are similar, yet different in their absorption numbers as well. With the Aeolian® being deeper with a single large cavity, it provides a bit more absorption in the low frequencies than the Model C, which is a more rigid geometry containing smaller elements. Depending on the space, this may be a useful addition to the diffusive properties. While some spaces need the extra absorption, some are pretty well balanced already and are just looking to “sweeten” the sound a bit.
On the surface, they are both a nominal 2’x2′ square of thermoformed Class A plastic with lightly textured surface. That is the extent of the visual similarities, and we cannot hide the aesthetic differences between the two devices. The ArtDiffusor® Model C is a “classic” diffuser. Many have been looking at these for the better part of 3 decades now. It’s a classic design at this point with no need for introduction – it is what the quintessential diffuser “looks” like. In fact, when many people think of a diffuser – the Model C is what they visualize! The Aeolian® is a modern rendition of the classic design. Using modern calculation techniques, we can now present the type of diffusion the Model C is famous for, in a different way.
While the two geometries look entirely different, and perform a bit differently, they have a common heritage as mathematical, 2-dimensional diffusers. You could say that the Model C is the grandparent of the Aeolian®, and that pedigree has been passed on – having a similar foundation, but a different final interpretation.
ArtDiffusor® Model C and Model F – Similar, yet different.
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Media Room, Music Tracking Room, Product Applications, Recording Facilities, Recording Studio, Studio Control Room, Theater, Uncategorized, Vocal Booth, Voice Over on August 20, 2020
We often get asked about the functionality of the different diffusers, and one of the frequently asked questions is about the differences between the ArtDiffusor® Model C and ArtDiffusor® Model F. We will cover some of similarities and differences in the design, functionality and use of these two devices.
Design.
The Model C and Model F use identical math to come up with their basic structure, they even have angled faces – the main difference between the two is that the Model F elements are ½ of the Model C’s height, length and width – and then it is duplicated 4 times in the same footprint… The Model C is nominally 2’ x 2’ x 4” deep. The Model F is four quadrants that are nominally 1’ x 1’ x 2” deep – like little scaled down Model C’s… This makes them visually similar and aesthetically compatible. This low profile design makes the Model F more desirable for ceiling installs in spaces with very limited headroom – like basement studios that have low ceilings.
Performance
Due to the different size of the elements on the two devices, they have very different frequencies at which they are most effective. The Model C is a mid-frequency diffuser by design… having larger elements and deeper wells than the Model F. The Model F is primarily a high-frequency diffuser, due to the small elements and lower profile. Both diffusers are tuned to different frequencies as their “primary range,” and while they do affect lower and higher frequencies than they are designed for – it is to a lesser degree, or the product of absorption.
What does this mean?
The Model C has a primary design range of 1KHz to 4KHz. This is where it is primarily designed to work. It can and does diffuse below 1KHz and over 4KHz – just to a lesser degree than its primary design range.
The Model F has a primary design range of 2KHz to 8KHz, and again, it does diffuse outside of that range, but to a lesser degree.
The angled caps of both the Model C and Model F help to extend their high frequency range by reflecting sound in different directions at higher frequencies – causing the sound to scatter spatially. The different heights of the elements cause sound reflections to be offset “temporally,” or in time. The sound that hits the higher elements is reflected sooner than the sound that hits the lower elements – travelling further before it is reflected. This time offset, changes the “Phase Coherency” of the reflection; the larger the difference in the heights, the greater the offset in time.
The size of the elements matters as well. The shorter wavelengths of high frequencies can diffract and scatter off of the smaller elements of the Model F more readily than low frequencies, which see the Model F as a slightly angled & mostly flat surface. However, the lower frequencies are more affected by the larger and deeper elements of the Model C.
How do these differences help define their use?
The Model C is a great all around diffuser – it covers a wide range of frequencies, throws a very predictable 2D diffusion pattern, and it is tuned to a very musical range.
The Model F is a great high-frequency diffuser. It targets a few very specific, yet important issues. High frequencies are responsible for some nasty problems in rooms. Flutter echoes, ringing, comb filtering, and other artifacts are particularly noticeable in higher frequencies. If your room is otherwise performing well acoustically, the Model F can help tackle that last hurdle to make a good room into a great room.

Many critical listening environments use both the Model C and Model F to tune the diffusion in their space.

While the white Aeolians® on the back wall are the visual focal-point on in Big3 Studio A, look closely at the ceiling and you will notice a large array of black Model C’s and Model F’s. These help to intermix the diffusion of different frequencies in the large control room.
Due to their aesthetic and functional compatibility, many rooms benefit from using both. Model C’s addressing the bulk of the Mid-range diffusion, and the Model F smoothing out the top end.
I hope that this highlights the unique properties of both the ArtDiffusor® Model C & ArtDiffusor® Model F – and helps to demystify their function and use in your space.


You must be logged in to post a comment.