Posts Tagged diffuser
Big vs. Bigger: 2′ vs 4′ Acoustic Diffusers
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Product Applications, Products on December 16, 2025
A couple common form factors in acoustics are based on building material sizes. Ceiling grids are a common place to install acoustic devices, and you will find that many are built to either work in a 2’x2′, 2’x4′, or 4’x4′ ceiling grid installation. This makes sense, but did you know that these devices also perform differently in some cases due to their dimensions? This is especially true with acoustic diffusers.
When you’re tuning a room—whether it’s a studio, theater, rehearsal space, or even a high-end listening room—acoustic diffusers are one of those rare tools that improve clarity without taking the life out of the space. Designs like the Double Duty Diffuser, Pyramidal Diffusers, and Quadratic Diffusers all share that same mission: redistribute sound energy so your room feels open, natural, and honest.
But while they may look similar in concept, their size changes the game. A 2’x2′ panel and a 4’x4′ panel both diffuse sound, but their effect—especially in the low-frequency and low-mid ranges—can be very different.
2’x2′ Diffusers — Compact Control
2’x2′ units are the most modular diffusers in the lineup. Their smaller footprint makes them ideal for:
- Breaking up mid and high-frequency reflections
- Treating small and medium rooms
- Sitting comfortably in grid ceilings or tight wall spaces
Because of their size, 2’x2′ diffusers don’t interact as much with the low-frequency energy in a room. Bass waves—being physically large—tend to wrap around smaller objects. The result? Excellent clarity improvements in the mids and highs, with a very predictable diffusion performance. The Double Duty Diffuser and Pyramidal diffusers have been a standard in breaking up planar surfaces for decades. While their diffusion in low frequencies is limited at this size, the air cavities do help control some upper bass frequencies through absorption.
The tuned mid frequency effects of the 2’x2′ quadratic, and the smooth performance of the Double Duty or Pyramidal diffuser are perfect for control rooms, edit rooms, drum booths, and anywhere you want accuracy without sacrificing sparkle.

4’x4′ Diffusers — Where Diffusion meets Bass Control
Now we get to the big ones.
A 4’x4′ diffuser is similar in concept to its smaller relatives, but the scale moves it into a different acoustic category. At this size, diffusers begin to influence longer wavelengths, which opens the door to something smaller diffusers often struggle with…
Low-frequency interaction
Large diffusers present enough depth, volume, and surface area to affect the bass spectrum. The extra size creates cavities which are tuned to reduce bass, and they have surfaces large enough to redirect those lower frequencies.
- Break up standing waves in the low-mid range
- Reduce modes and nodes common in rectangular rooms
- Add a sense of openness to the bass field
- Prevent buildup behind listening positions
In other words: same diffuser concept, very different low-end behavior.
Wide-area coverage
A single 4’x4′ panel can modify a huge portion of a wall, creating an even, spacious character that feels less like “treatment” and more like a room that’s naturally well-behaved.
These panels shine in larger studios, live rooms, and worship spaces—anywhere you need diffusion that reaches deeper into the frequency spectrum – and can break-up large, flat, specular surface reflections, which are responsible for flutter, echoes, bass buildup, and long reverb times.
Which do you need?
There are two main factors in the decision: space and performance requirements. In certain environments, it’s impractical or impossible to install large 4’x4′ or larger diffusers; It also may not be the best solution – even if it may appear to be on paper. While a single, large barrel diffuser may appear ideal, you may not have enough physical space to allow the diffusion to develop – where several smaller diffusers would be the better solution.
In short, your physical space and acoustic conditions will dictate which size elements will give you the most benefit in your environment.

You say “Diffuser,” I say “Diffusor”
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Q&A, Uncategorized on November 11, 2025
If you’ve spent any time around acoustic treatment—especially sound diffusion—you’ve probably noticed something odd: sometimes the product is called a “diffuser“, and other times it’s a “diffusor“. For newcomers, this can feel like a secret code or a subtle technical distinction – But the truth is much simpler.

Many trace the dual spelling back to Manfred Schroeder, the German physicist who developed the mathematically designed Quadratic Residue Diffusor (QRD).
In German, the word is spelled “Diffusor.” When Schroeder’s work entered the academic world, the spelling likely came with it.
Because his research became foundational in architectural acoustics, the German spelling spread through physics papers, textbooks, and graduate-level acoustics programs. Over time, “diffusor” became a common spelling when discussing mathematical or Schroeder-style diffusors specifically.
As manufacturers began producing these mathematically derived designs—like the ArtDiffusor® line from Acoustics First® (and many other early products)—they retained the “diffusor” spelling as a nod to the academic and scientific origins.
Before long, the industry ended up with two spellings that referred to the same thing:
- Diffuser – the standard English spelling
- Diffusor – the academically inherited, German-influenced spelling tied to Schroeder’s work
Both spellings appear throughout the professional audio world, and both are correct.
Is There Any Practical Difference?
No. None. Zero.
There is no technical difference between a “diffuser” and a “diffusor.” They both refer to devices used to redistribute sound energy and improve the acoustic quality of a space through accelerating the development of sound field diffusion. The spelling variation is purely linguistic.
Think of it like “colour” vs. “color” or “flavour” vs. “flavor.” British English keeps the “u,” American English drops it. (However, if you ask a Brit, they’ll tell you Americans are obviously spelling it wrong.)
The “diffusor/diffuser” split works the same way—just with a German twist.
So Which Should You Use?
Use whichever feels natural or matches the context you’re writing in. Many engineers and academics use “diffusor” when referring to Schroeder-type or other mathematical designs, simply out of tradition. Others stick with the standard English “diffuser.”
Tomato. Tom-ah-to.
Similar, yet different: Angled QRD vs. Standard QRD
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Product Applications, Products on August 19, 2025

In this installment of “Similar, yet Different,” we explore the similarities and subtle differences between a classic, standard 1D QRD and a modern, angled 1D QRD. While being based on the same mathematic function for their design, there are a couple subtle differences in the performance of these devices.
Quick review. A Quadratic Residue Diffuser is based on a mathematic equation that states that the Well Depth is decided based on the square of the position of the cell and the remainder of when it is divided by a prime number. (We know it sounds really complex… but this is how the ratios of the wells are calculated to maintain a balance of magnitude across the face of the device.)
The equation looks like this:
Well Depth = (n² modulo p)
(Note: there will not be a quiz!)
As it was stated, both of the devices use the identical calculation when coming up with their wells… but there is one important change – the well bottoms are flat on the standard QRD and angled on the angled quadratic. This change makes this diffuser perform differently in 2 key ways:
- The Diffusion Pattern is wider on the angled QRD.
- There is a more subtle transition from one frequency to the next on the angled QRD.

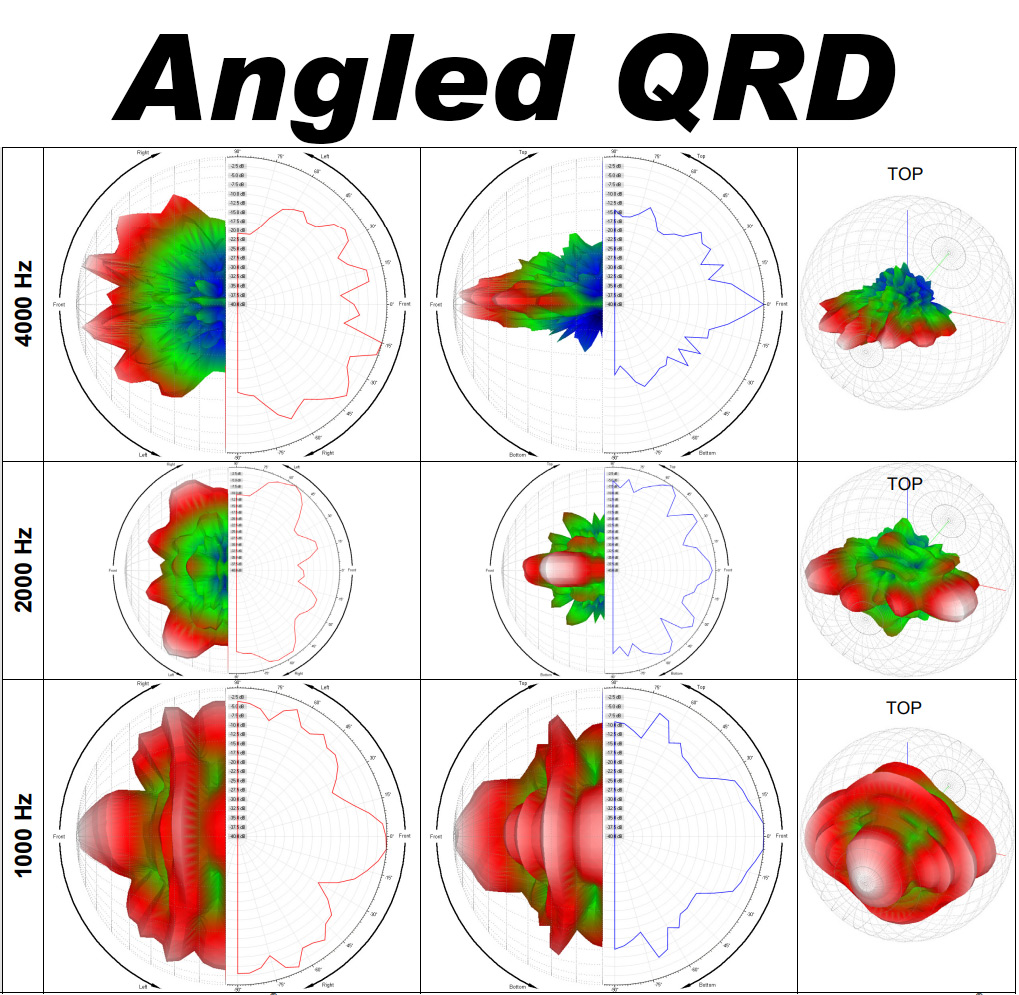
When you look at the two sets of polar pattern above, you will notice that the Angled QRD has a wider pattern, as shown in the first-column, horizonal polar pattern (at 2000Hz especially), where the standard QRD is a more forward-focused pattern.
What does that mean in practice?
Both of these diffusers have a 1D pattern, but the flat bottoms of the standard QRD primarily use diffraction and incidence angle to widen the diffusion… the rest of the diffusion works on the principal of phase offset from the depth of the wells and the time of travel. The Angled QRD introduces an angle which means that one side of the well is deeper than another. This changes the reflection angle, time of travel, and, in turn, degrees of phase shift depending on where the sound strikes the inside of the well. This modification smooths the transition of phase from well to well – as the wells themselves have a range of phase change. This angle also causes the sound to be redirected toward the inner walls of the wells, causing it to change direction from the angle of incidence – widening the pattern further, changing the travel time, and basically bouncing sound around more.
There are some situations where the standard QRD‘s narrow pattern and well-defined transition frequencies may be preferable. In some practice rooms or larger listening spaces, there may be a need for the diffusion to be a little more directional, maybe to hit (or avoid) a certain position in the room. In these scenarios, the standard quadratic may be the recommended choice. In other spaces where you want the reflections to spread out more rapidly – maybe in smaller rooms or spaces where you need to get more coverage from ceiling reflections – then the angled quadratic may be more appropriate.
In closing, while these two devices have a nearly identical design, a small difference can have a big effect on the performance of the diffuser – and how you use them.
Similar, yet different: HiPer Panel® vs. HiPer Panel® Impact
Posted by Acoustics First in Absorption, Diffusion, Product Applications, Products on December 11, 2024
While the HiPer Panel® and the HiPer Panel® Impact may appear to be identical on the surface, there are some key differences that may change which one you would use, and why you would use it. They are both layered, flat-panel diffuser products, with perforations, and they are both covered in fabric. However, their construction, below the surface, is drastically different. One is a broadband absorber with a modified frequency response which focuses on reduction of specular energy, and cancellation of noise – where the other is a high frequency diffuser and reflector with a tuned bass absorption which is constructed to maintain acoustic energy in the space.

Construction
The HiPer Panel® was originally designed to optimize the capabilities of a standard broadband absorber. Its internal membrane and perforations create a material that works to modify the range of absorption, and create high frequency diffraction… but that isn’t all. The cavities are backed up to the membrane, which changes the reflection characteristics, where high frequencies can be reflected, and higher energy waves are absorbed more than if it was just fiberglass. This extended range is random, as the perforation density is gaussian in nature, but the membrane is also randomly backed by more cavities.
This design creates 4 different physical conditions that acoustic energy has to contend with… in a gaussian distribution.
- areas of the panel with 2 layers of fiberglass and a membrane in the middle.
- one layer of fiberglass with a rear membrane over a cavity.
- a cavity with a membrane back… sitting on fiberglass.
- a cavity with a membrane back… stretched over another cavity.
The random distribution of multiple acoustic obstacles is what gives this device its unique characteristics. It’s an absorber that changes its performance depending on where sound hits it, and at which frequency. Some frequencies pass into the cavities and reflect off the membrane, while others are dampened by the membrane… while longer wavelengths see the membrane as a stretched diaphragm or limp mass.
The HiPer Panel® Impact has a very different construction and may be used for a very different reason. The HiPer Panel® Impact uses the same pattern of holes, but the holes aren’t cut into an absorber… they are cut out of a reflective face, which is attached to an absober. Unlike the first HiPer Panel®, the “Impact” can be used to maintain more of the energy in the space, break up some of the higher frequencies with that gaussian hole pattern, and be a low frequency bass trap. The design is simple and effective, but is not necessarily used in the same places where you would use the first HiPer Panel®.
Use cases.
The first Hiper Panel® is often used in theaters, and listening spaces where focusing on the source is of primary importance. Its broadband absorption, gentle high frequency diffusion, and smooth mid frequency control are ideal for critical listening environments such as mixing rooms, media rooms, theaters, or even voice over spaces. The performance is about removing the acoustic elements that could interfere with the focus on the source speakers.
The HiPer Panel® Impact is often used in performance spaces, where you want to maintain energy, break up high frequency flutter, and remove low bass. The reflective face doesn’t remove as much energy from the space, however it does change the characteristics of the space. This helps break up some frequencies, reduce bass, and keep the energy moving around the room. Music halls, churches, auditoriums, and any space that relies on the room helping to reinforce the sound will benefit from these taking the edge off the highs and dampening the lows – which is how the HiPer Panel® Impact controls the sound… while helping it maintain its “impact.”
In summary, while these two products are in the same family, they have a different core construction, which changes their performance. There are scenarios where you may use them both, however since they address different problems in a space, they are not always interchangeable. Contact Acoustics First® if you have questions about any of our products.
Similar, yet Different: Pyramid vs. QuadraPyramid
Posted by Acoustics First in Articles, Product Applications, Products on November 15, 2024

Based on the golden-ratio, offset pyramid… both the Acoustics First® Pyramids and QuadraPyramids have a great deal in common. They are asymmetric in their scattering, which reduces lobing. They have different sized surfaces of different angles, which impose different polar radiation patterns at different frequencies. Both allow for redirection, while allowing much of the signal phase to remain intact, which keeps a great deal of energy moving together, which works great for performance spaces. However, there are some subtle differences which change how these units perform and how you maximize their use.
While both the Pyramidal and the QuadraPyramid come in a 2’x2′ format, the QuadraPyramid packs 4 pyramids into that footprint. That isn’t the only difference though. The depth of the QuadraPyramid is only about 2-3/4″ to the 8″ deep single peak of the classic Pyramidal. On top of that, the Pyramidal comes in different sizes and ratios of length to width including a 4’x4′ and a 2’x4′ at up to 13″ deep.
These different sizes do more than change their aesthetic. The large pyramid geometry allows for greater impact on lower frequencies, as the longer wavelengths are less skewed by small surfaces. The different ratios and sizes also changes the angle of throw off the surfaces, allowing for more options to redirect the sound. The larger surfaces also impose some limitations to their use. Being physically larger means that the listener will need to be further away from the device to allow the reflections to spread out, and the greater depth means that, at certain angles, the geometry can place other devices in their acoustic shadow. The larger pyramids work great in larger rooms with high ceilings, where they can be placed higher in the room. This makes them ideal for performance spaces and large band/music practice rooms – where everyone is spread around and needs to be able to hear everyone else.

The QuadraPyramids have a higher density of reflective faces per square foot. There are 16 facets on a 2’x2′ QuadraPyramid, which means more smaller faces to reflect sound. These faces are optimized for higher frequencies which have shorter wavelengths – but the profiles are actually better suited for smaller rooms with lower ceilings. In smaller studios, listening rooms, and media spaces, space is at a premium, and having a large diffuser hanging a foot down from the ceiling would be more of an impediment. This is where the QuadraPyramids shine. Their low-profile and many facets allow for sounds to spread out while breaking up flutter echoes and reducing other higher frequency artifacts.
Finally, the size of the cavity behind the larger pyramid allows for greater bass trapping, especially with the ability to fill the cavity with fluffy insulation. While the QuadraPyramid still imparts some absorption due to the resonance of the thermoformed plastic material, it is more focused at the resonant frequency (250Hz) – while the larger pyramids have a wider frequency range they affect.
| Device | 125hz | 250Hz | 500Hz | 1000Hz | 2000Hz | 4000Hz | NRC |
| 2’x2′ Pyramid (insulated) | 0.57 | 0.41 | 0.38 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.30 |
| 2’x2′ Quadra Pyramid | 0.23 | 0.58 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.20 |
While the Pyramid and the QuadraPyramid have their roots in the same geometry, their specific implementation changes their performance characteristics to provide more options in treating your space. Using the right treatment changes depending on the space and its function… even two identical rooms can have drastically different performance requirements – needing drastically different treatments. Acoustically, a Quadrapyramid is drastically different than a 2’x4′ Pyramid – but fundamentally, at their core, they are very similar.
You must be logged in to post a comment.