Posts Tagged QRD
Similar, yet different: Angled QRD vs. Standard QRD
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Product Applications, Products on August 19, 2025

In this installment of “Similar, yet Different,” we explore the similarities and subtle differences between a classic, standard 1D QRD and a modern, angled 1D QRD. While being based on the same mathematic function for their design, there are a couple subtle differences in the performance of these devices.
Quick review. A Quadratic Residue Diffuser is based on a mathematic equation that states that the Well Depth is decided based on the square of the position of the cell and the remainder of when it is divided by a prime number. (We know it sounds really complex… but this is how the ratios of the wells are calculated to maintain a balance of magnitude across the face of the device.)
The equation looks like this:
Well Depth = (n² modulo p)
(Note: there will not be a quiz!)
As it was stated, both of the devices use the identical calculation when coming up with their wells… but there is one important change – the well bottoms are flat on the standard QRD and angled on the angled quadratic. This change makes this diffuser perform differently in 2 key ways:
- The Diffusion Pattern is wider on the angled QRD.
- There is a more subtle transition from one frequency to the next on the angled QRD.

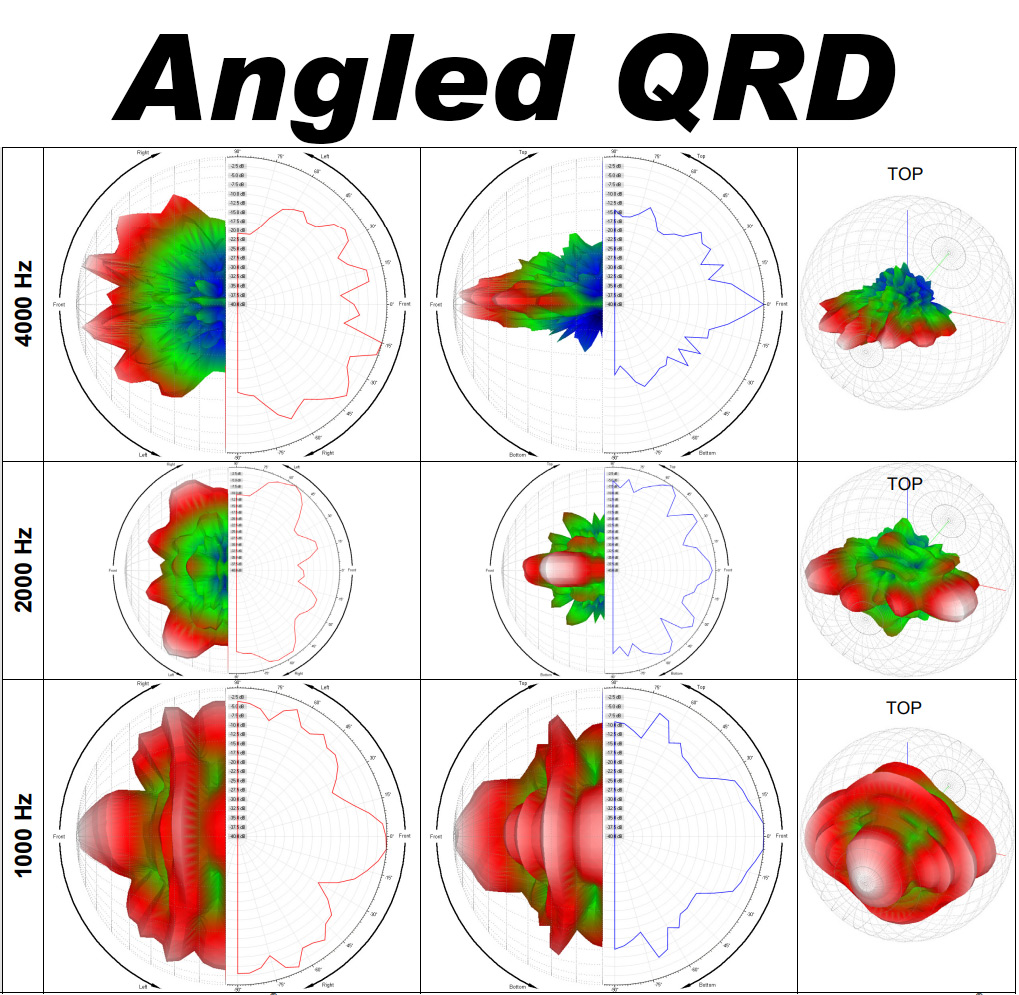
When you look at the two sets of polar pattern above, you will notice that the Angled QRD has a wider pattern, as shown in the first-column, horizonal polar pattern (at 2000Hz especially), where the standard QRD is a more forward-focused pattern.
What does that mean in practice?
Both of these diffusers have a 1D pattern, but the flat bottoms of the standard QRD primarily use diffraction and incidence angle to widen the diffusion… the rest of the diffusion works on the principal of phase offset from the depth of the wells and the time of travel. The Angled QRD introduces an angle which means that one side of the well is deeper than another. This changes the reflection angle, time of travel, and, in turn, degrees of phase shift depending on where the sound strikes the inside of the well. This modification smooths the transition of phase from well to well – as the wells themselves have a range of phase change. This angle also causes the sound to be redirected toward the inner walls of the wells, causing it to change direction from the angle of incidence – widening the pattern further, changing the travel time, and basically bouncing sound around more.
There are some situations where the standard QRD‘s narrow pattern and well-defined transition frequencies may be preferable. In some practice rooms or larger listening spaces, there may be a need for the diffusion to be a little more directional, maybe to hit (or avoid) a certain position in the room. In these scenarios, the standard quadratic may be the recommended choice. In other spaces where you want the reflections to spread out more rapidly – maybe in smaller rooms or spaces where you need to get more coverage from ceiling reflections – then the angled quadratic may be more appropriate.
In closing, while these two devices have a nearly identical design, a small difference can have a big effect on the performance of the diffuser – and how you use them.
Eight very different 2′ x 2′ sound diffusers.
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Product Applications, Products, Recording Facilities on June 30, 2025
Acoustics First® has maximized the idea of adaptable designs. One of the most common modular architectural elements is the 2′ x 2′ ceiling grid. While standard, fiber ceiling tiles have their uses, specialized acoustic environments require higher-performing materials – for both absorption and diffusion. While Acoustics First® excels with its Sonora® and Cloudscape® Ceiling tiles, today we are going to focus on the wide range of 2’x 2′ diffusers that have been developed over the several decades.
Sound diffusers in a 2′ x 2′ format have several advantages, other than just being placed in a ceiling grid to help diffuse the ceiling. They integrate well on walls and in arrays, where they can help break up large flat surfaces and help minimize flutter and standing waves from parallel surfaces. While they provide many different aesthetic options, there are also many different functional types of diffusers available in this form-factor to address different acoustic issues, from flutter, bass issues, targeted frequency absorption, and geometric scattering. Let’s look at some of these devices and their uses.
Geometric Diffusers.
Geometric diffusers have been around a long time. These devices break up large flat surfaces and redirect or “scatter” those reflections in different directions. They work great in environments where you need to redirect acoustic energy in a predictable way, and redistribute a specular reflection over a wider area. In a 2′ x 2′ size, you can also get a fair amount of bass absorption, due to the large cavity behind the geometric shapes creating a space that can be stuffed with absorbent material to tune it.

Quadratic/Mathematic Diffusers
Mathematic diffusers are devices that use specific calculations to design their size, shape, and structures to effect their performance. A common type is called the Quadratic Residue Diffuser (sometimes called a Schroeder Diffuser, after its pioneering inventor, Manfred Schroeder). This type uses a Quadratic Residue Sequence that optimizes uniform sound diffusion at specific design frequencies. There are different ways to implement these designs, but two common designations are based on their diffusion patters – 1D or 2D. A 1D Quadratic diffuser mostly spreads energy in one plane, and a 2D provides a hemispheric pattern.



Organic Diffusers.
Organic diffusers are a variation on the classic mathematic diffusers which use different mathematic functions to optimize the diffusion further by creating a smooth transition. Once such method is called Bicubic Interpolation. Instead of having the math restricted to having blocks at certain heights, the interpolation bridges these heights using a function that provides a smooth transition to the next target height. This transition creates unlimited resolution in the frequencies within it’s functional range, providing expanded uniformity throughout its range, and increasing its capabilities. As different frequencies are affected differently depending on their wavelength – the organic diffusers have no hard edges to define their pattern and look differently to different frequencies and energy from varied sources.


These diffusers all have the ability to be used in different types of installations for different reasons. Many of these diffusers are mixed and matched in the same room. You will see these on the walls or ceiling, and placed in different locations. There are rooms with Double-Duty diffusers for low frequency control, Model C for Mids, and Model F for flutter, while other rooms may have Aeolians™ on the rear wall and Model C’s and Model F’s to control the ceiling.

Keep in mind, these aren’t even all the diffusers we have available, these are just the ones specific to the 2′ x 2′ format. The Aeolian™ has a 1′ x 1′ version called the Aeolian™ Mini. There are flat panel diffusers that are hybrid absorbers and diffuser like the HiPer Panel® and the HiPer Panel® Impact. There are even large format versions of the Double Duty™ diffuser, Pyramidal, and even the Quadratic Diffuser.
For more info about these diffusers, read some of our, “Similar, Yet Different Series,” where we go into more detail about our products… and how some of these are similar, yet different!”
If you have any questions as to which products you need to optimize your space, reach out to Acoustics First® and we can help you find which products will be best for your application. Remember that Acoustics First’s® full line of sound diffusers are all made in the USA, with many available in stock for quick shipping.
Acoustics First® makes sound Visible!
Posted by Acoustics First in Diffusion, Product Applications, Products, Uncategorized, Video on November 18, 2016
 As many of you know, Acoustics First® invests a great deal of energy in the development of the science of acoustics. Here are three ways that we are making advances that help people learn and actually Visualize acoustics!
As many of you know, Acoustics First® invests a great deal of energy in the development of the science of acoustics. Here are three ways that we are making advances that help people learn and actually Visualize acoustics!
Those interested in sound diffusers have certainly noticed that Acoustics First® has produced a Diffuser Data book, containing all kinds of test data about how our diffusers contribute to the sound in your space. This information is a great advancement and we have worked closely with the ASTM committee developing this test method. Some people wonder exactly how the test produces the data that we report, and we have developed a simulation to show exactly how the sound energy is sampled during this test.
If you download the Diffuser Data booklet, you can see a picture of the gigantic test arc at NWAA Labs which is used for the real world tests.
Acoustics First – Diffuser Data Test Demo from Acoustics First®.
We have also made leaps and bounds in using simulations to show the different ways that diffusion develops in a space. Depending on the type and placement of the diffusers you install, the diffuse field will develop at different speeds, at different frequencies. We can now show a couple of simulations of the development of a diffuse field to help you visualize how sound moves in room without treatment and with two different sets of diffuser treatments.
Acoustics First – Room Simulations from Acoustics First®.
Bonus video! Imagine being able to see the Untreated room and the Model D room from a different angle – To be able to move around the outside of the room and see how the sound field develops from a different perspective. Imagine no more! Here it is!
Acoustics First – Sound Field Development Simulation – 3D Panning from Acoustics First®.
If you prefer to use YouTube – you will find the videos uploaded at our YouTube channel here.
We hope these helped you to “look” at acoustics in a whole new way, and stay tuned – more advancements are coming soon!
Contact Acoustics First® for a high bitrate, presentation quality version of the videos – as well as permission and terms of use.
Bonus! Simulations! Now in stereo – and with absorption! Click Here!
You must be logged in to post a comment.